Diet, Longevity and Blue zones
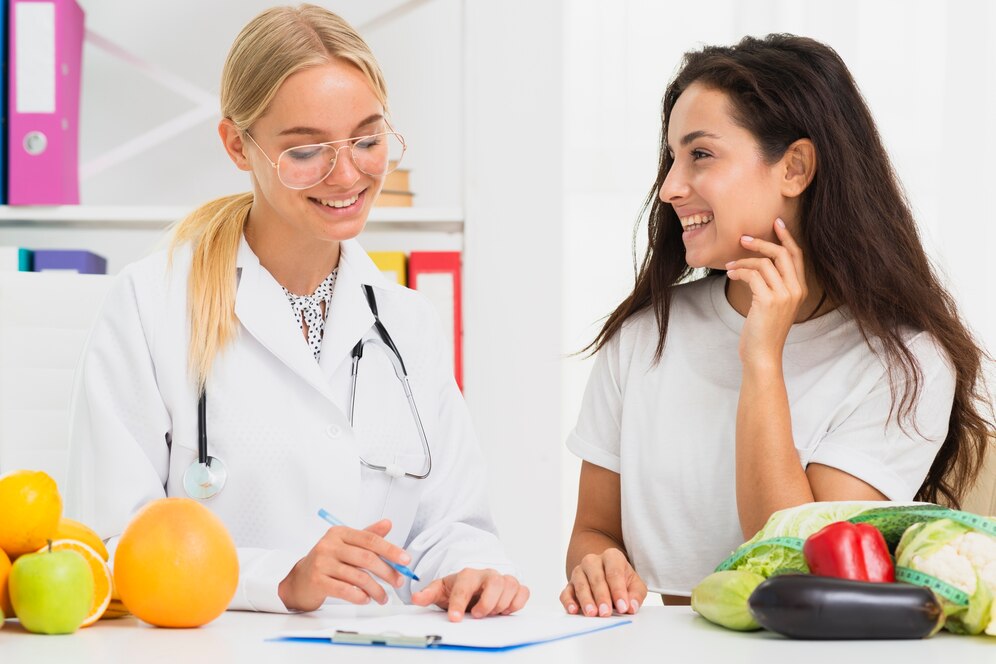
Increasing life expectancy is a major challenge in public health. World Health Organization has proposed a model of healthy aging which is composed of psychological and sensory function vitality, locomotion cognition, etc. The process of aging is complex, several factors like behavioral, environmental along with dietary factors affect this process and finally define whether one would develop disease in late life. These factors influence specific pathways that regulate the processes which are responsible for longevity. To establish the relationship between a healthy aging and healthy diet we need data, (epidemiological and clinical data).
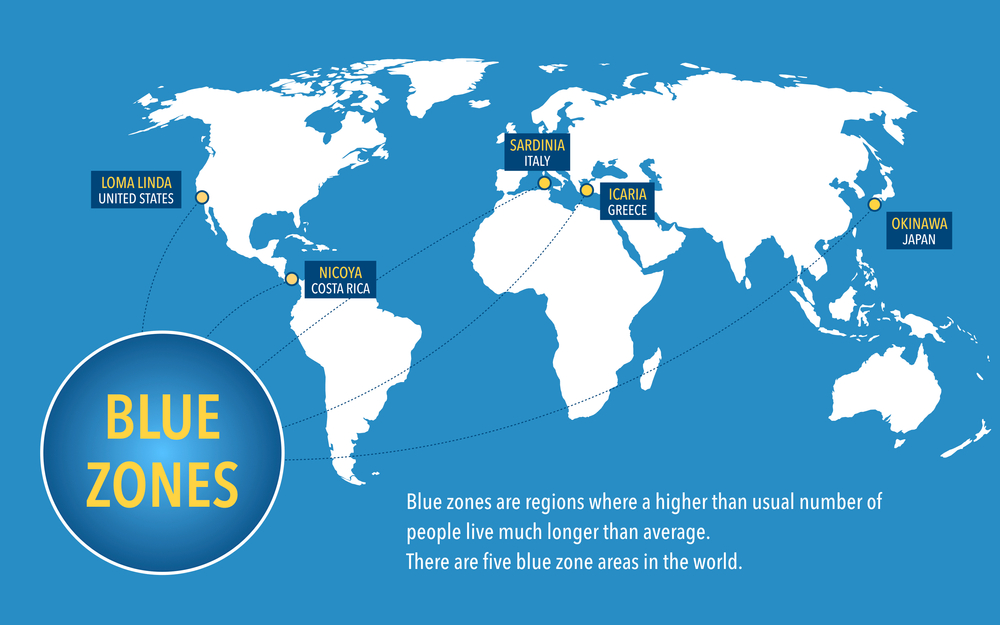
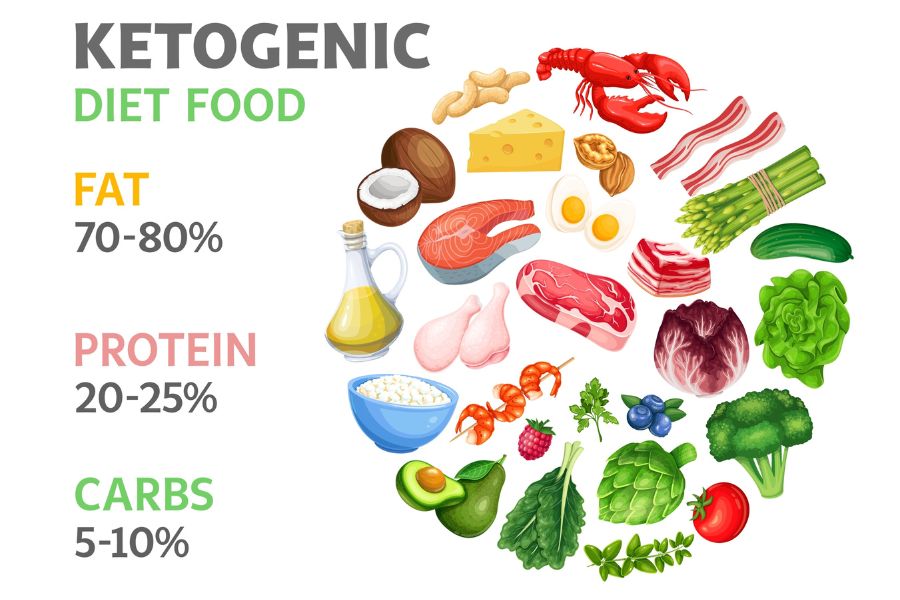
Over the past century, there have been significant changes in nutrition research. The focus was to link nutritional deficits to disease identification or management. The former reductionist approach directed to understanding the molecular and cellular mechanism associated with single nutrients, now has developed into a more comprehensive objective of identifying the function of the different combinations of the food. Not the food element alone, the eating model is also associated with environmental, social, behavioral, geographical, and cultural factors that significantly impact on maintaining health and preventing diseases.


How Menopause Affects Gut Health
Menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end of a woman’s reproductive years, typically occurring in her late 40s or early 50s. The gut microbiome, which refers to the community of microorganisms living in the digestive tract, has been a topic of increasing interest in relation to various aspects of health, including menopause. Some studies have suggested potential links between the gut microbiome and menopausal symptoms and health outcomes. Lower levels of Estrogen have been shown to influence the composition and diversity of the gut microbiome. As Estrogen plays a role in maintaining bone density, so indirectly bone health is also connected to gut microbiome. Some research suggests a potential connection between the gut-brain axis and mood changes or cognitive function during menopause. The gut microbiome may influence the production of certain neurotransmitters that impact mood and cognitive function. Changes in the composition of the gut microbiome may also have implications for vaginal health, as alterations in microbial balance can affect susceptibility to infections.
Aging conditions supportive nutrition is based on structural functional scientifically proven claims and also time tested healing foods used in various culinary cultures and healing systems.
|
Aging Conditions |
Food / Herbs / Nutritional Supplements |
| Blood Sugar | Fenugreek, Alpha Lipoic Acid, Jamun, Product Options > |
| Blood Pressure | Green Tea,Ubiqunol, Product Options > |
| Cognition | Ginkgo Biloba Product Options > |
| Memory | Bacopa Monnieri Product Options > |
| Menopause/PMS | Soy Isoflavones,Evening primrose oil,Asparagus Racemosus, St John’s Wort,Black Cohosh,Wild Yam,Flax seed, Magnesium , Vitamin D Product Options > |
| PCOD/PCOS | Asparagus Racemosus,Myo-inositol Product Options > |
| Dementia/Alzaimers | Curcumin, Product Options > |
| Sleep | Melatonin,Mucuna Pruriens,Valerian, Product Options > |
| Arthritis / Pain | Boswellia Serrata,Curcumin,Ginger, Product Options > |
| Osteoporosis | Ciccus,Moringa, Product Options > |
| Fatty Liver | MilkThistle,N-acetylCysteine, Product Options > |
| Cholesterol | Green Tea, Product Options > |
| Obesity | Caralluma,Garcinia,L-Carnitine, Product Options > |
| Prostate / BPH |
Tribulus,Saw Palmetto, Product Options > |
| Skin dry/wrinkles | Marine collagen, Hyaluronic acid, Product Options > |
| Hair fall | V Millets,Biotin,Bamboo shoots, Product Options > |
| Healthy Aging | Trans-Resveratrol, Astaxanthin, Ubiqunol,Tocotrienols,Blue green algae, AFA, Methyl folate,Niacin Product Options > |






